SKYWAVE: Enhancing Real-Time Performance in Digital Communications using Machine Learning

Project Overview
Funding: ARDC (Amateur Radio Digital Communications)
Duration: 2025-2029
Role: Principal Investigator
Institution: University of Leeds, School of Computing
The SKYWAVE project explores the synergy between artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and real-time distributed (RTD) systems, using wireless communication and amateur radio as experimental platforms. Our research hypothesis is that AI and ML can provide quantitative insights into the likelihood of successful message transmissions over wireless channels by analyzing previously sent messages, thereby reducing uncertainty in real-time communication schedulers.
Research Objectives
The project aims to develop a transmission scheduler that leverages machine learning insights to optimize HF (High Frequency) communications. Our key objectives include:
- Dataset Creation: Build comprehensive FT8 datasets from multiple HF bands (20m, 17m, 40m, 15m) to train ML models
- ML Model Development: Train models that can predict transmission success based on channel conditions
- Intelligent Scheduler Design: Create a real-time scheduler that uses ML predictions to optimize transmission parameters
- Validation: Test and validate the system through simulation and real-world deployments
The focus is on producing models and algorithms that can execute on small devices with limited processing and storage capabilities, making them suitable for IoT and amateur radio applications.
Key Components
1. FT8 Dataset Collection Tool (FT8DC)
We have developed FT8DC (FT8 Dataset Creator), an automated tool for creating FT8 datasets. The tool operates by:
- Listening to an FT8 band for a specified duration using WSJT-X
- Transmitting CQ calls on the same frequency
- Querying PSK Reporter to identify which stations received the transmission
- Logging all relevant metrics including SNR, timestamps, and propagation data
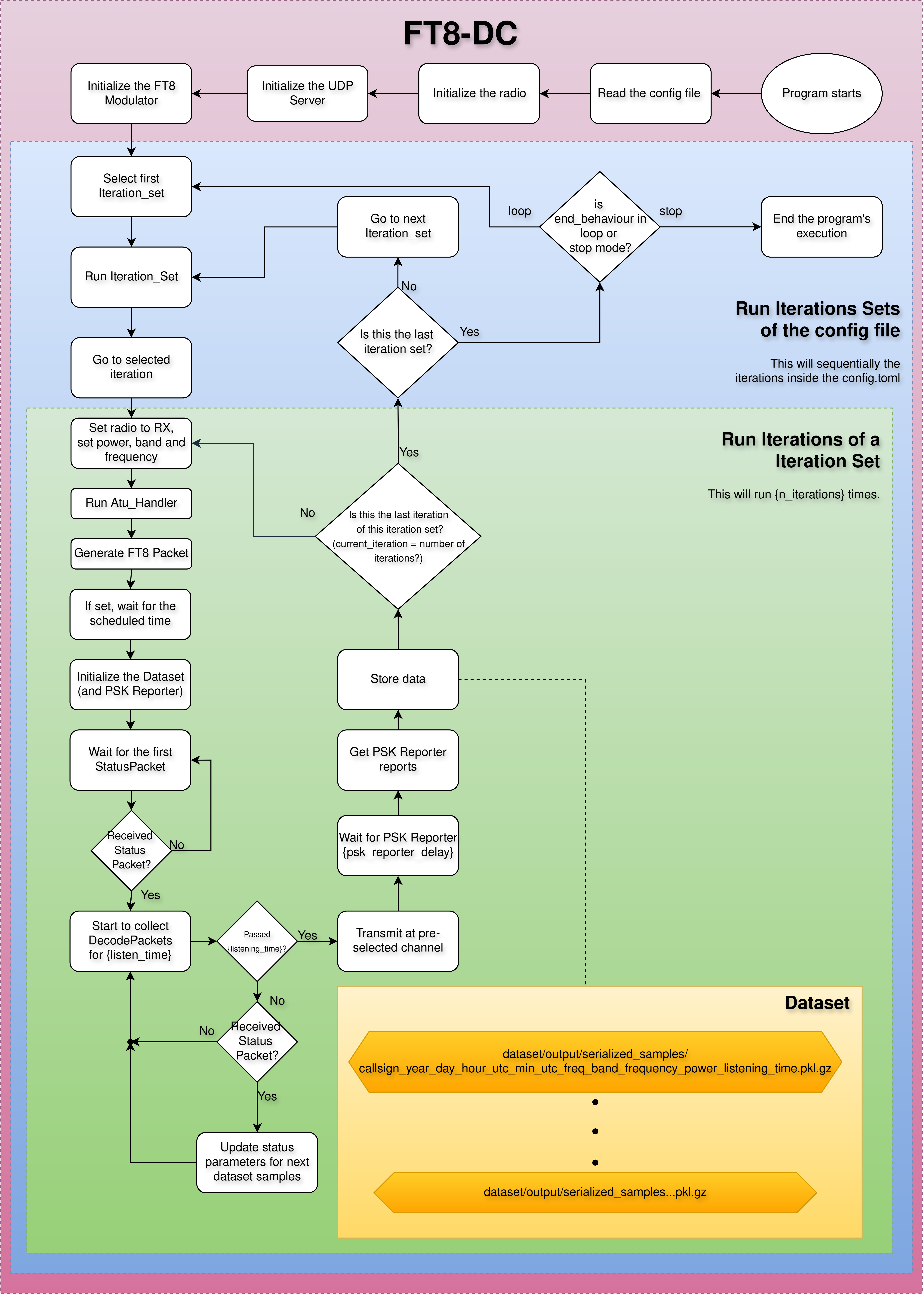
Figure 1: FT8DC program execution workflow showing the three main stages of data collection
Data Collection Bands:
- 20m (14 MHz)
- 17m (18 MHz)
- 40m (7 MHz)
- 15m (21 MHz)
2. Feature Extraction Pipeline
Our approach extracts relevant features from received FT8 messages to predict transmission success. The feature extraction process analyzes:
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) distributions
- Time offset variations (DT)
- Number and geographic distribution of receiving stations
- Temporal patterns in message reception
- Band conditions and propagation characteristics
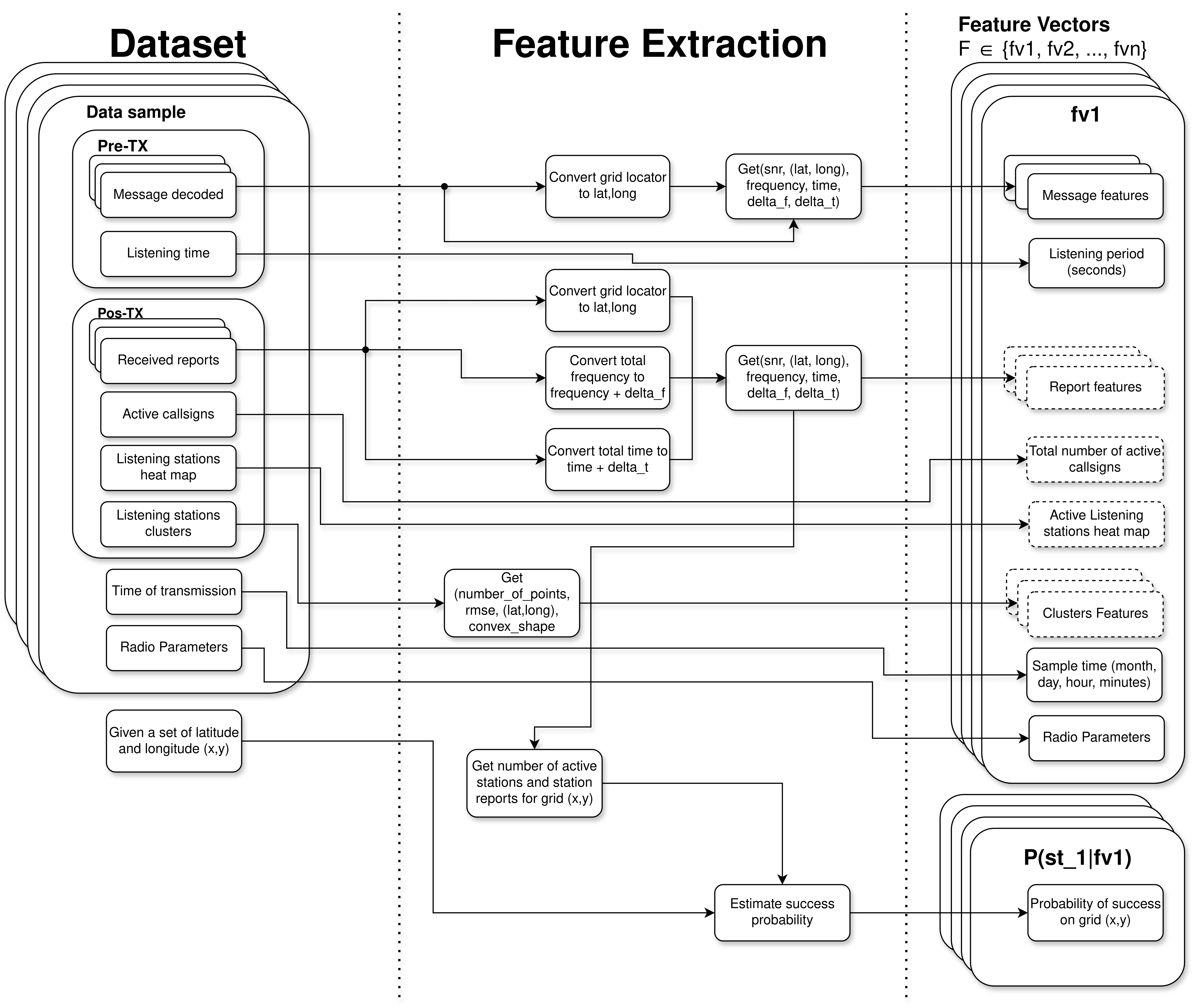
Figure 2: Feature extraction pipeline from received FT8 messages
3. ML-Assisted Scheduler Architecture
The scheduler integrates machine learning predictions with real-time decision-making to optimize transmission parameters such as frequency selection, power levels, timing, and retransmission strategies.
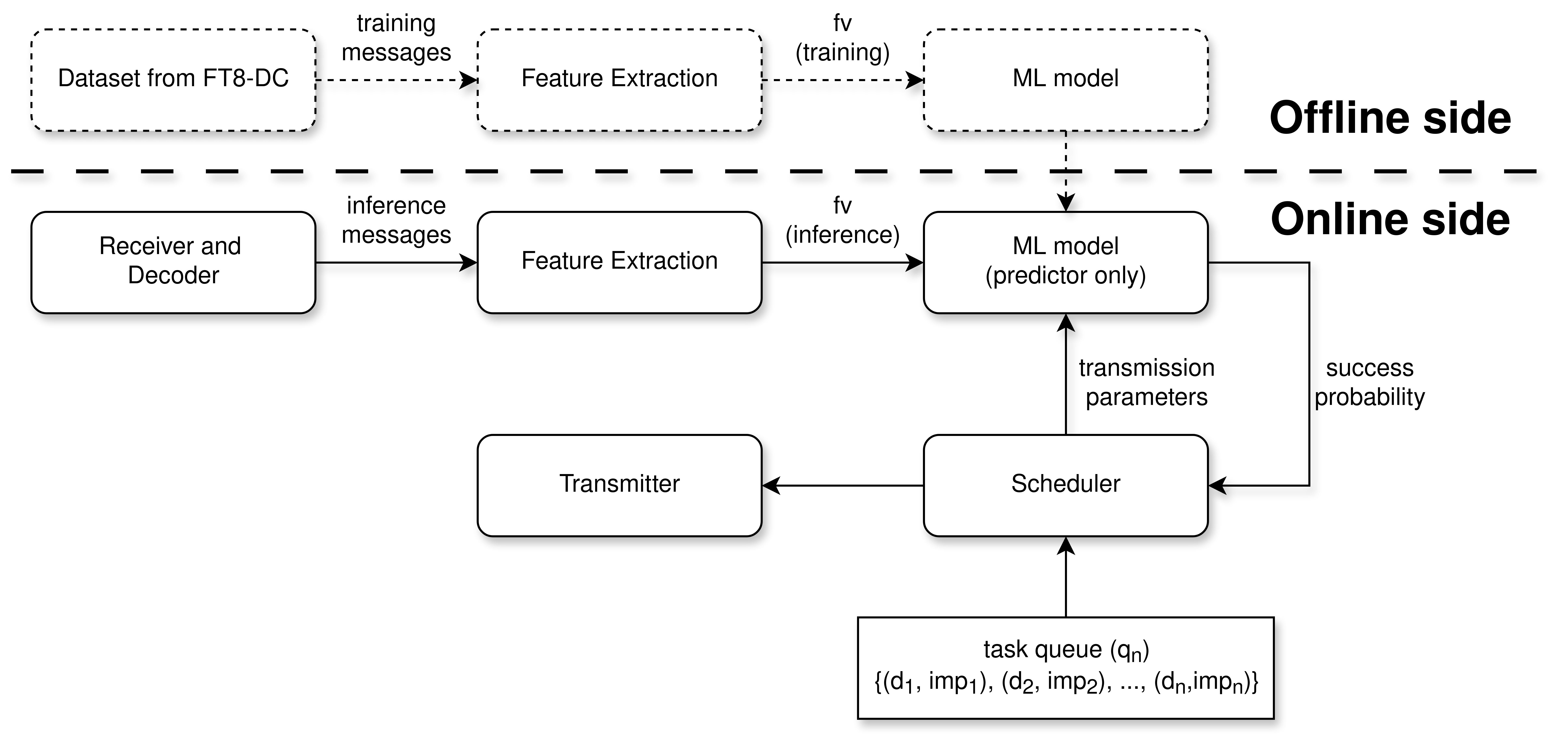
Figure 3: Architecture showing how the ML model interacts with the real-time scheduler
Research Methodology
The project follows a three-stage approach:
Training Stage
- Collect large datasets using FT8DC across multiple HF bands
- Extract features from received messages and correlate with transmission success
- Train ML models (neural networks, deep learning) to recognize patterns
- Validate model accuracy through cross-validation and testing
Deployment Stage
- Integrate lightweight ML models into the transmission scheduler
- Use real-time channel observations to feed the ML model
- Scheduler makes decisions based on ML predictions and RTD constraints
- Provide statistical guarantees for message delivery (e.g., 90% success rate for high-priority messages)
Evaluation Stage
- Develop simulation environment to test scheduler performance
- Deploy system in real amateur radio stations for field testing
- Compare performance against traditional propagation models
- Iterate and refine based on results
Expected Outcomes
- Open Datasets: Multiple FT8 datasets with thousands of entries, publicly available
- Software Tools: FT8DC and related tools for dataset creation, feature extraction, and ML model training
- ML Models: Pre-trained models for HF propagation prediction, optimized for resource-constrained devices
- Scheduler Algorithms: Novel real-time scheduling algorithms under uncertainty
- Publications: Academic papers in real-time systems, wireless communications, and ML conferences
- Community Resources: Documentation and tutorials for amateur radio operators
All datasets, software, and publications will be made publicly available following open science principles.
Team
Principal Investigator: Prof Leandro Soares Indrusiak (G5LSI)
PhD Student: Miguel Boing (M7NSE)
Assessor: Prof Zheng Wang (University of Leeds)
The project is part of the Distributed Systems and Services research group at the University of Leeds School of Computing.
Impact
This project benefits both the academic community and amateur radio operators by:
- Advancing state-of-the-art in ML-assisted real-time scheduling
- Providing data-driven propagation prediction models
- Enabling autonomous and intelligent amateur radio stations
- Supporting performance optimization for contest stations and emergency communications
- Creating tools for quantitative comparison of station configurations
Related Links
Contact
For more information about this project, please contact Prof Leandro Soares Indrusiak at L.SoaresIndrusiak@leeds.ac.uk
